前言
从今天开始我们进入Spring Boot的源码解读系列,本次使用的源码版本为3.2.X,后续默认都用这个版本的源码做解读。
我们先看一个最简单的Spring Boot启动代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
就这么几行代码就成功启动了一个Spring Boot项目,我们今天就盘一下它是如何启动的。我们从run方法点进去,最终可以看到这样一个方法,总结来说就是先创建一个SpringApplication的实例,然后调用这个实例的run方法。
1
2
3
| public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
|
先看下这个流程图,以对整个流程有个大体的了解。
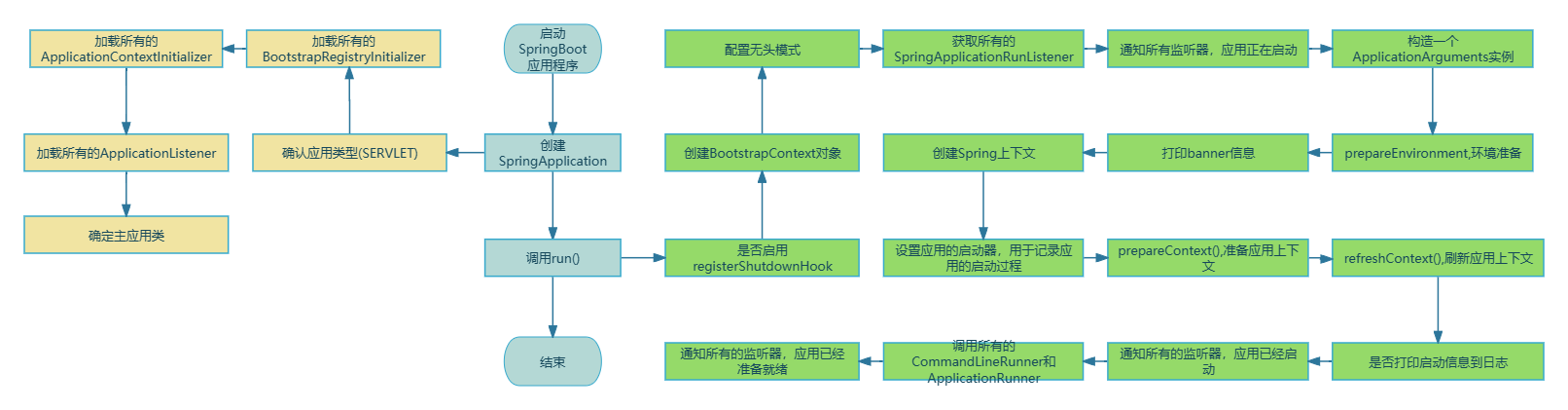
创建SpringApplication实例的过程
这个构造函数的主要作用是创建一个新的SpringApplication实例,并初始化其各种属性和组件。
总得来说,构造SpringApplication实例的时候,会确认应用类型,并从META-INF/spring.factories加载各种属性和组件,然后确认主应用类, 这样就完成了Spring Boot启动的第一步
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
|
SpringApplication.run()流程
run()是Spring Boot应用启动的主要入口,内部逻辑十分庞大,包括但不限于创建Spring容器,创建bean,启动tomcat等等,都放在这一章去讲无疑是不现实的,所以我们这次只梳理主要流程,并确定run()方法中每步都是用来干什么的。内部方法我们不会深入,后面会开单独的文章去解读他们的过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
Startup startup = Startup.create();
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
SpringApplication.shutdownHook.enableShutdownHookAddition();
}
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
startup.started();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), startup);
}
listeners.started(context, startup.timeTakenToStarted());
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
listeners.ready(context, startup.ready());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
|
其中,refreshContext(context);方法是如此重要,所以我们现在这里看下它的大概逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
|
可以看到,它最后调用的是Spring提供的refresh方法,我们继续看内部逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| @Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
this.startupShutdownLock.lock();
try {
this.startupShutdownThread = Thread.currentThread();
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
initMessageSource();
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
onRefresh();
registerListeners();
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
finishRefresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex ) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
destroyBeans();
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
finally {
this.startupShutdownThread = null;
this.startupShutdownLock.unlock();
}
}
|
@SpringBootApplication的作用
在Spring Boot的启动类中我们会发现它被标注了一个@SpringBootApplication,那么它是用来干什么的?简单来说,它只是一个组合注解,但是它内部三个核心注解却是Spring Boot启动过程中扮演着不可或缺的角色。
@SpringBootConfiguration
@SpringBootConfiguration继承了@Configuration,所以它拥有@Configuration注解的所有特性。这个注解的作用主要是表示当前类是一个配置类。
@ComponentScan
它的作用是启动组件扫描,然后Spring就会知道需要在哪些包以及子包中进行扫描。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
它的主要作用是启动Spring Boot的自动配置机制,在它内部还有两个重要功能,他们都是自动配置的一部分
@AutoConfigurationPackage
它用于标记一个包为自动配置包。当你在一个类上添加@AutoConfigurationPackage注解时,Spring Boot会自动扫描这个类所在的包以及子包,查找所有的配置类,并将这些类作为自动配置的候选者。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
这是一个ImportSelector的实现,它的主要作用是选择所有需要自动配置的类。它会读取META-INF/spring.factories文件,查找所有的自动配置类,然后根据条件选择需要导入的类。这些类会被Spring框架自动注册到Spring上下文中,然后根据这些类的定义创建和初始化bean。







%20(%E5%B0%8F).jpg)
.jpg)