懒加载定义 什么是Mybatis的懒加载机制?简单来说就是在使用时才会触发查询操作,而不是在一开始就加载所有数据。懒加载机制只在有子查询时生效,一定程度上可以提升程序的响应能力。
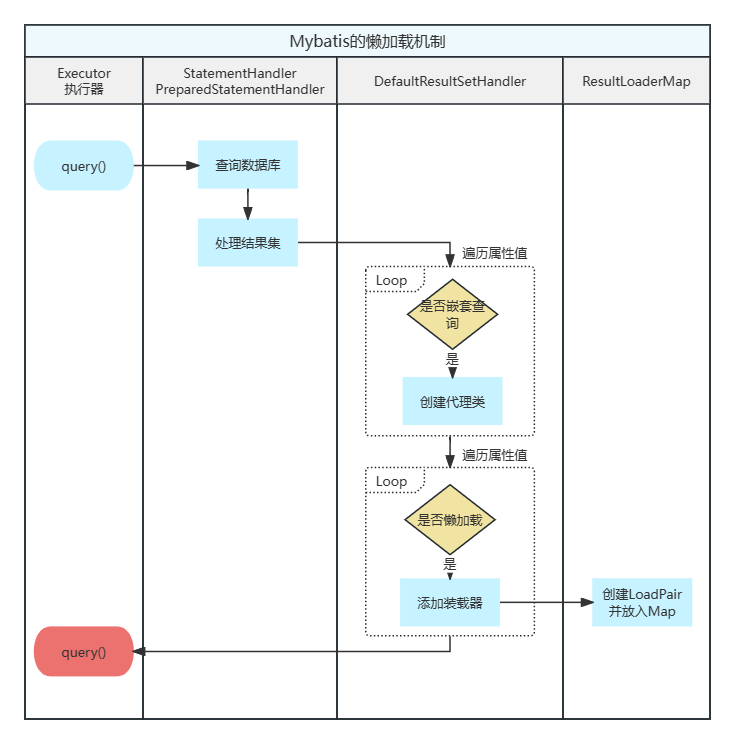
懒加载的整体结构
测试程序 还是基于Blog和Comment的测试程序,简单调整一下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="org.example.mybatis_reader.mybatis.blog.BlogMapper" > <resultMap id ="BlogMap" type ="org.example.mybatis_reader.mybatis.blog.BlogPO" autoMapping ="true" > <id column ="ID" property ="id" jdbcType ="INTEGER" /> <result column ="TITLE" property ="title" jdbcType ="VARCHAR" /> <collection property ="comments" column ="id" select = "selectCommentByBlogId" fetchType ="lazy" /> </resultMap > <resultMap id ="commentMap" type ="org.example.mybatis_reader.mybatis.blog.CommentPO" autoMapping ="true" > <id column ="ID" property ="id" jdbcType ="INTEGER" /> <result column ="BLOG_ID" property ="blogId" jdbcType ="INTEGER" /> <result column ="CONTENT" property ="content" jdbcType ="VARCHAR" /> </resultMap > <select id ="selectBlogById" resultMap ="BlogMap" > SELECT * FROM T_BLOG WHERE ID = #{id} </select > <select id ="selectCommentByBlogId" resultMap ="commentMap" > SELECT * FROM T_COMMENT WHERE BLOG_ID = #{id} </select > </mapper >
测试类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class BlogPOTest { private Configuration configuration; private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; @Before public void init () { SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder (); sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(BlogMapper.class.getResourceAsStream("/mybatis-config.xml" )); configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration(); } @Test public void test1 () { BlogMapper blogMapper = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(BlogMapper.class); BlogPO blogPO = blogMapper.selectBlogById(1L ); System.out.println("===================================" ); System.out.println("执行其它大段逻辑" ); System.out.println(blogPO.getComments()); } }
看下测试结果,可以看到在执行访问操作时,才触发了查库操作,说明懒加载机制已经生效。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [main] DEBUG o.a.i.t.jdbc.JdbcTransaction - Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@5cc69cfe] [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.BlogMapper.selectBlogById - ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM T_BLOG WHERE ID = ? [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.BlogMapper.selectBlogById - ==> Parameters: 1(Long) [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.BlogMapper.selectBlogById - <== Total: 1 =================================== 执行其它大段逻辑 [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.B.selectCommentByBlogId - ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM T_COMMENT WHERE BLOG_ID = ? [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.B.selectCommentByBlogId - ==> Parameters: 1(Long) [main] DEBUG o.e.m.m.b.B.selectCommentByBlogId - <== Total: 1 [CommentPO{id =1, blogId=1, userId=1, content='你说的对'}]
实现原理 属性赋值的流程中是如何兼容懒加载机制的? 在处理结果集的过程中,如果某个ResultMapping是嵌套查询并且声明了懒加载,那么会先为它创建一个代理;在后续流程中会构建一个LoadPari并放入到ResultLoaderMap类的一个HashMap中。
简单看下这部分的源码:
DefaultResultSetHandler 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private Object createResultObject (ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException { this .useConstructorMappings = false ; final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList <>(); final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList <>(); Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix); if (resultObject != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) { final List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings(); for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) { if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null && propertyMapping.isLazy()) { resultObject = configuration.getProxyFactory().createProxy(resultObject, lazyLoader, configuration, objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs); break ; } } } this .useConstructorMappings = resultObject != null && !constructorArgTypes.isEmpty(); return resultObject; }
继续流程,依旧是getNestedQueryMappingValue方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private Object getNestedQueryMappingValue (ResultSet rs, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultMapping propertyMapping, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException { if (nestedQueryParameterObject != null ) { } else { final ResultLoader resultLoader = new ResultLoader (configuration, executor, nestedQuery, nestedQueryParameterObject, targetType, key, nestedBoundSql); if (propertyMapping.isLazy()) { lazyLoader.addLoader(property, metaResultObject, resultLoader); value = DEFERRED; } else { value = resultLoader.loadResult(); } } } return value; }
接着看ResultLoaderMap部分的逻辑,这里主要是构建LoadPair并将其维护在一个HashMap中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private final Map<String, LoadPair> loaderMap = new HashMap <>();public void addLoader (String property, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultLoader resultLoader) { String upperFirst = getUppercaseFirstProperty(property); if (!upperFirst.equalsIgnoreCase(property) && loaderMap.containsKey(upperFirst)) { throw new ExecutorException ("Nested lazy loaded result property '" + property + "' for query id '" + resultLoader.mappedStatement.getId() + " already exists in the result map. The leftmost property of all lazy loaded properties must be unique within a result map." ); } loaderMap.put(upperFirst, new LoadPair (property, metaResultObject, resultLoader)); }
可以看到整个流程还是很简单的。
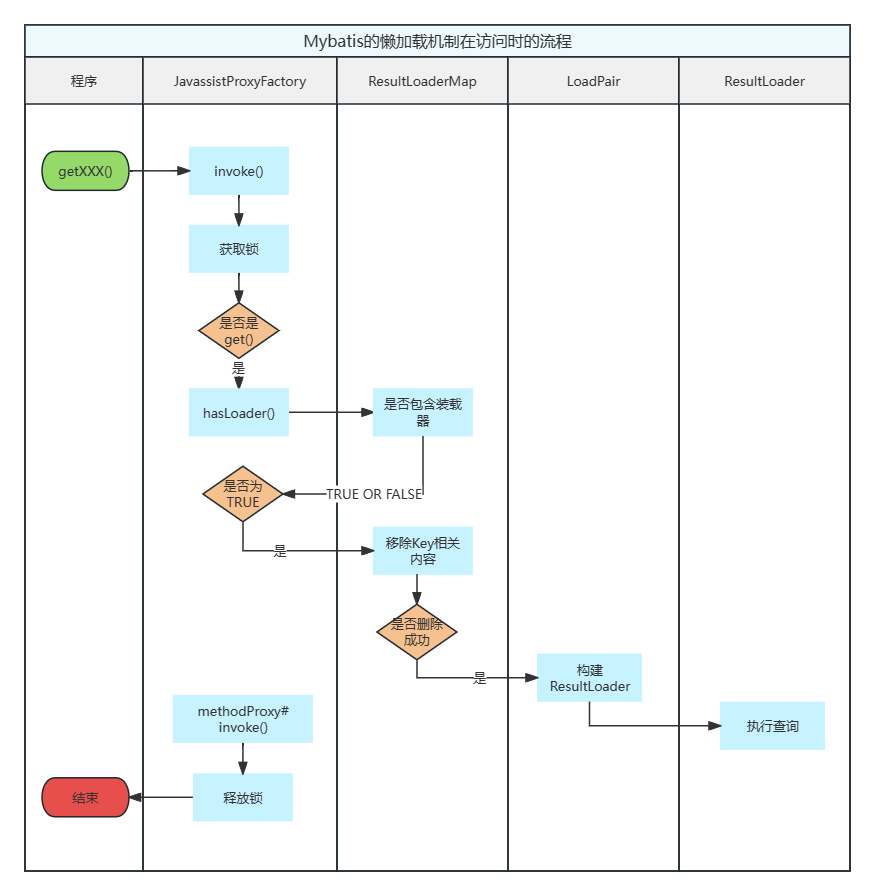
访问时如何触发查询的呢? 现在我们看下在访问属性时,是如何通过代理完成查询的:
也简单看下源码。
JavassistProxyFactory 因为是代理类,直接看invoke方法总归是不会错的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 @Override public Object invoke (Object enhanced, Method method, Method methodProxy, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final String methodName = method.getName(); lock.lock(); try { if (WRITE_REPLACE_METHOD.equals(methodName)) { Object original; if (constructorArgTypes.isEmpty()) { original = objectFactory.create(type); } else { original = objectFactory.create(type, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs); } PropertyCopier.copyBeanProperties(type, enhanced, original); if (lazyLoader.size() > 0 ) { return new JavassistSerialStateHolder (original, lazyLoader.getProperties(), objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs); } else { return original; } } if (lazyLoader.size() > 0 && !FINALIZE_METHOD.equals(methodName)) { if (aggressive || lazyLoadTriggerMethods.contains(methodName)) { lazyLoader.loadAll(); } else if (PropertyNamer.isSetter(methodName)) { final String property = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(methodName); lazyLoader.remove(property); } else if (PropertyNamer.isGetter(methodName)) { final String property = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(methodName); if (lazyLoader.hasLoader(property)) { lazyLoader.load(property); } } } return methodProxy.invoke(enhanced, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
看下懒加载器中的load方法的逻辑,可以看到它会先将这个属性的结果处理器从懒加载器中删除,这意味着不论后续加载过程是否成功,我们再执行get()方法时也不会触发查库操作了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public boolean load (String property) throws SQLException { LoadPair pair = loaderMap.remove(property.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); if (pair != null ) { pair.load(); return true ; } return false ; } public void load (final Object userObject) throws SQLException { if (this .metaResultObject == null || this .resultLoader == null ) { if (this .mappedParameter == null ) { throw new ExecutorException ("Property [" + this .property + "] cannot be loaded because " + "required parameter of mapped statement [" + this .mappedStatement + "] is not serializable." ); } final Configuration config = this .getConfiguration(); final MappedStatement ms = config.getMappedStatement(this .mappedStatement); if (ms == null ) { throw new ExecutorException ( "Cannot lazy load property [" + this .property + "] of deserialized object [" + userObject.getClass() + "] because configuration does not contain statement [" + this .mappedStatement + "]" ); } this .metaResultObject = config.newMetaObject(userObject); this .resultLoader = new ResultLoader (config, new ClosedExecutor (), ms, this .mappedParameter, metaResultObject.getSetterType(this .property), null , null ); } if (this .serializationCheck == null ) { final ResultLoader old = this .resultLoader; this .resultLoader = new ResultLoader (old.configuration, new ClosedExecutor (), old.mappedStatement, old.parameterObject, old.targetType, old.cacheKey, old.boundSql); } this .metaResultObject.setValue(property, this .resultLoader.loadResult()); }
ResultLoader 最后是调用Executor的query()方法执行具体的查询动作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public Object loadResult () throws SQLException { List<Object> list = selectList(); resultObject = resultExtractor.extractObjectFromList(list, targetType); return resultObject; } private <E> List<E> selectList () throws SQLException { Executor localExecutor = executor; if (Thread.currentThread().getId() != this .creatorThreadId || localExecutor.isClosed()) { localExecutor = newExecutor(); } try { return localExecutor.query(mappedStatement, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, cacheKey, boundSql); } finally { if (localExecutor != executor) { localExecutor.close(false ); } } }
总结 Mybatis的懒加载机制有助于我们优化程序性能,而且要使用它也很简单,只需要在对应的xml中添加fetchType=”lazy”就能开启懒加载机制。
它的实现原理也很清晰。简单来说就是在结果集处理结果时,如果我们开启了懒加载并且ResultMapping还是一个嵌套查询,那么就会为这个属性创建代理方法;随后为这个属性构造一个结果处理器并放入到懒加载中的集合属性中。在我们的程序访问这个属性时会,代理类会调用懒加载器的laod()方法,然后懒加载会从它的集合中移除这个属性对应的结果处理器,然后由结果处理器调用执行的queyr()方法完成查询操作。
.png)


.jpg)

%20(%E5%B0%8F).jpg)

.jpg)


%20(%E5%B0%8F).jpg)